Overview
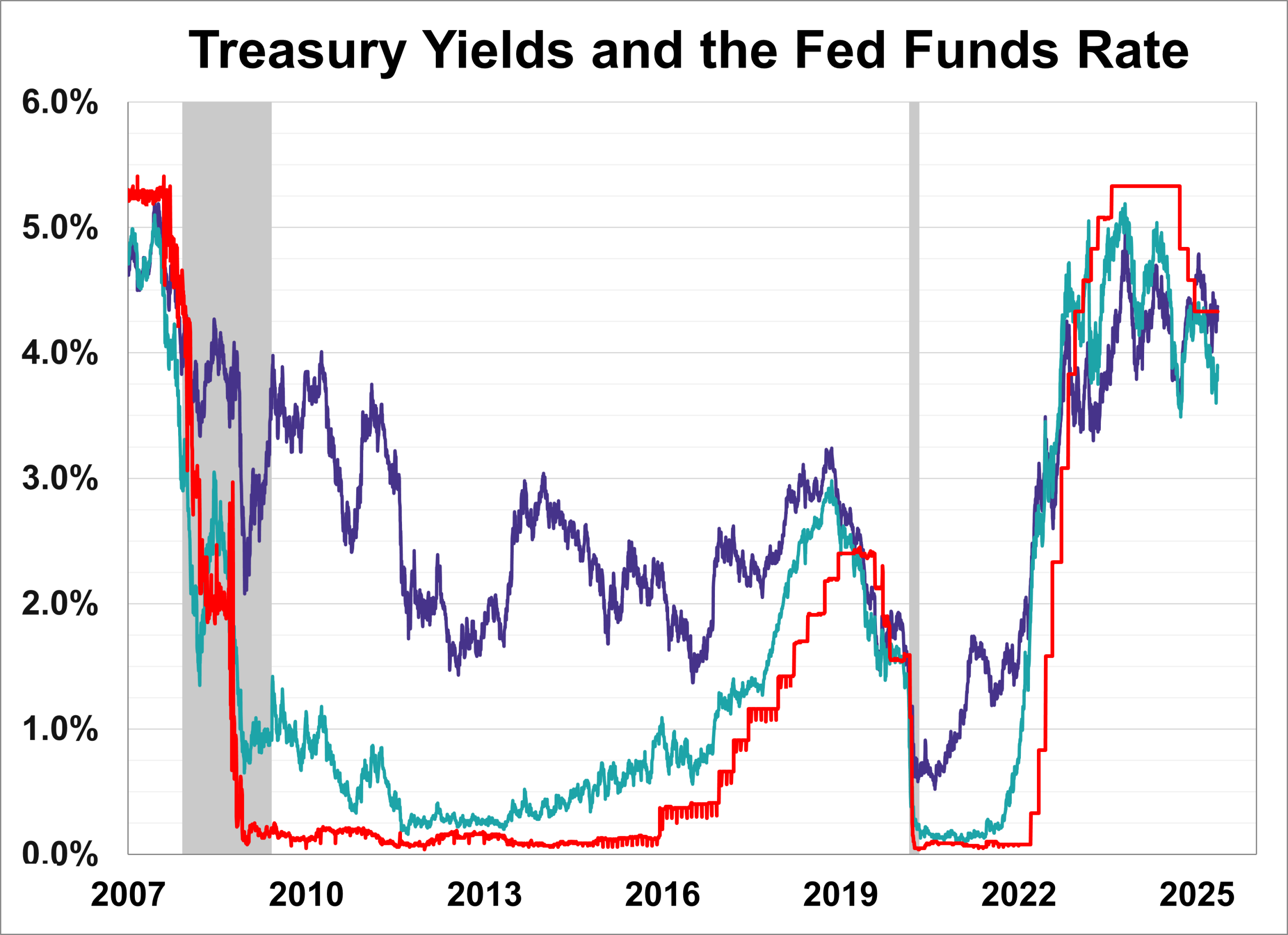
The Federal Reserve’s decision on May 7, 2025, to pause its string of rate hikes has sent immediate ripples through the U.S. Treasury market. Short-term yields held near multi-year highs, while longer-term Treasury rates, especially the 10-year note, ticked lower as investors reassessed future Fed policy expectations. This “twist” in the yield curve reflects shifting growth and inflation outlooks, influences mortgage and corporate borrowing costs, and offers clues on when the Fed may resume rate cuts. Below, we unpack the drivers behind this move, examine its impact on various maturities, and outline what investors should watch next.
1. Why the Fed Hit Pause
The Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) opted to maintain its federal funds rate at 4.25%–4.50%, citing heightened uncertainty around trade policy and mixed economic data (Reuters). Chair Jerome Powell emphasized the need for additional evidence on inflation cooling and labor market stability before altering policy. With headline CPI easing to 3.4% year-over-year and non-farm payrolls still expanding, the Fed chose a “steady as she goes” approach to balance growth and price stability (Reuters).
2. Immediate Impact on Treasury Yields
2.1 Short-Term vs. Long-Term
- Short-Term Yields: The 2-year Treasury yield held near its peak of 4.40%, reflecting persistent expectations that the Fed will keep policy restrictive for longer (交易经济).
- Long-Term Yields: The 10-year yield dipped to around 4.05%, down from 4.25% pre-announcement, as bond traders priced in potential rate cuts later this year (WSJ).
This divergence led to a modest steepening of the yield curve—a sign that markets now see lower rates on the horizon even as short-term rates stay elevated .
2.2 Sectoral Effects
- Mortgage Rates: With the 30-year Treasury yield easing slightly, average fixed-rate mortgages edged down by 5 basis points to 6.75% (WSJ).
- Corporate Bonds: Investment-grade spreads tightened by 3 basis points as issuers took advantage of lower long-term rates to lock in funding (MarketWatch).
3. Underlying Drivers
3.1 Inflation Expectations
Market-based measures of inflation compensation, such as the 5-year breakeven rate, fell from 2.8% to 2.6% on the pause news, signaling easing price-rise fears (Schwab Brokerage).
3.2 Growth Outlook
Surveys of economists now project U.S. GDP growth at 1.8% for 2025—down from earlier 2.1% forecasts—fueling demand for longer-duration Treasuries as a safe haven (晨星).
3.3 Fed Communications
Powell’s press remarks highlighted a data-dependent framework (“we’re not on a preset path”), which markets interpreted as more dovish than previous forward guidance (Reuters).
4. What Investors Should Watch
- Next CPI & PCE Reports: Further deceleration in core inflation could cement expectations for Fed cuts later this year (U.S. Bank).
- Treasury Auction Demand: Oversubscription at upcoming 10- and 30-year auctions will reveal appetite for long-dated debt amid heavy issuance (MarketWatch).
- Yield Curve Movements: A sustained steepening may signal renewed confidence in economic resilience; an inversion could warn of recession risks .
- Fed Dot Plot Updates: The June FOMC meeting’s updated projections will offer fresh insights into policymakers’ rate-cut timing .
Conclusion
The Fed’s pause marks a pivotal juncture: short-term rates remain anchored at restrictive levels, while long-term yields reflect growing optimism that inflation is under control. This recalibration has broad implications—from loan pricing to portfolio allocations—and sets the stage for careful monitoring of key economic releases and Fed signals in the months ahead.